Combination IL-15
Patients with relapsed/refractory mature T-cell cancers may be eligible to participate in a new clinical trial at the NIH Clinical Center.
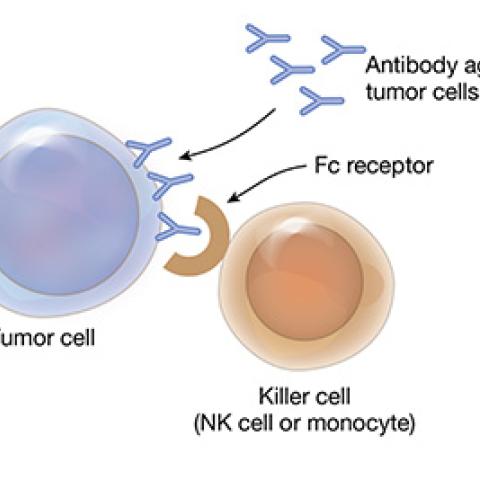
Mature T-cell cancers are a group of fast-growing lymphomas and leukemias. They begin in T cells that have matured in the thymus gland and then spread to other sites in the body. Mature T-cell cancers do not respond well to standard treatments. Milos Miljkovic, M.D., M.Sc., of the Lymphoid Malignancies Branch, is testing a combination treatment for patients whose mature T-cell cancer has returned after therapy or has not responded to therapy. Avelumab is an immunotherapy agent that enhances the activity of immune cells and blocks a protein pathway that allows cancer cells to hide from the immune system. Thus, avelumab helps the immune system detect and attack cancer cells. Patients will also receive interleukin-15 (IL-15), a protein that signals many types of immune cells to multiply and go on the attack against cancer cells. Investigators want to determine the safety and best dose of intravenous avelumab and IL-15 for patients with mature T-cell cancers.
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT03905135
NCI Protocol ID: NCI-19-C-0076
Official Title: A Phase 1 Study of Interleukin-15 in Combination With Avelumab (Bavencio) in Relapsed/Refractory Mature T-cell Malignancies
The Center for Cancer Research is NCI’s internal cancer center, a publicly funded organization working to improve the lives of cancer patients by solving important, challenging and neglected problems in cancer research and patient care. Highly trained physician-scientists develop and carry out clinical trials to create the medicines of tomorrow treating patients at the world’s largest dedicated research hospital on the campus of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland.
For more information on CCR clinical trials click here, and subscribe to have the latest CCR clinical trials sent directly to your inbox.